Cornea and Lasik Eye Surgeon Specialist & Opthalmologist in Dombivali
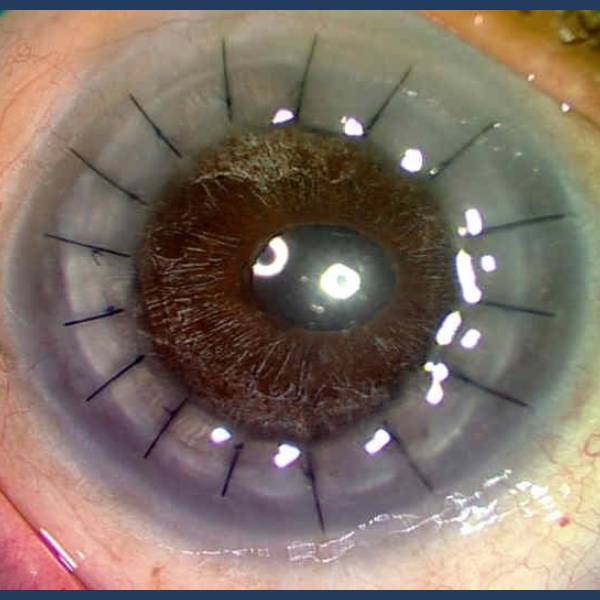
Cornea Transplantation
Cornea transplantation, also known as corneal transplantation or keratoplasty, is a surgical procedure in which a damaged or diseased cornea is replaced with healthy corneal tissue from a donor. The cornea is the clear, dome-shaped surface at the front of the eye that helps to focus light and provide clear vision.
Cornea transplantation may be recommended for people who have a damaged or diseased cornea that is causing vision loss or other problems. The most common indications for cornea transplantation include corneal scarring, corneal thinning, corneal dystrophies, and corneal edema.
During the procedure, the damaged or diseased cornea is carefully removed and replaced with healthy donor tissue. The transplantation is performed under local anesthesia, and the procedure typically takes several hours. After the surgery, the patient will need to rest and avoid strenuous activities for a period of time to allow the eye to heal.
Cornea transplantation can be an effective treatment for people with a damaged or diseased cornea. The success rate for cornea transplantation varies, but many people experience improved vision after the procedure. However, there are some risks associated with the surgery, including the possibility of rejection of the donor tissue, infection, or bleeding. It is important to discuss the risks and potential benefits of the procedure with an ophthalmologist before undergoing cornea transplantation.
Types of Cornea Transplantation are:
Copyright © All Rights Reserved, By Dr Vidya Bawkar
 WhatsApp
WhatsApp